The year 2026 began with an unexpected economic anomaly: a sudden, unprecedented surge in demand for the Apple Mac mini. This spike was not driven by a new product launch or a holiday sale, but by a viral open-source project called Clawdbot (now it is renamed to Moltbot for potential trademark dispute). Across social media platforms like X and Reddit, screenshots of Mac mini setups, often stacked in small, personal data centers, were accompanied by sensational claims: "I built my entire website while watching Netflix" or "It cleared 10,000 emails from my inbox while I was asleep". The phenomenon was so pronounced that even Google executive Logan Kilpatrick publicly announced his purchase of the compact desktop, solidifying the trend.
I checked its GitHub stats and they are absolutely insane. In just 20 days, the stars skyrocketed from a few hundred to over 40K. Even more mind-blowing—it gained a massive 30K stars in a single day yesterday.
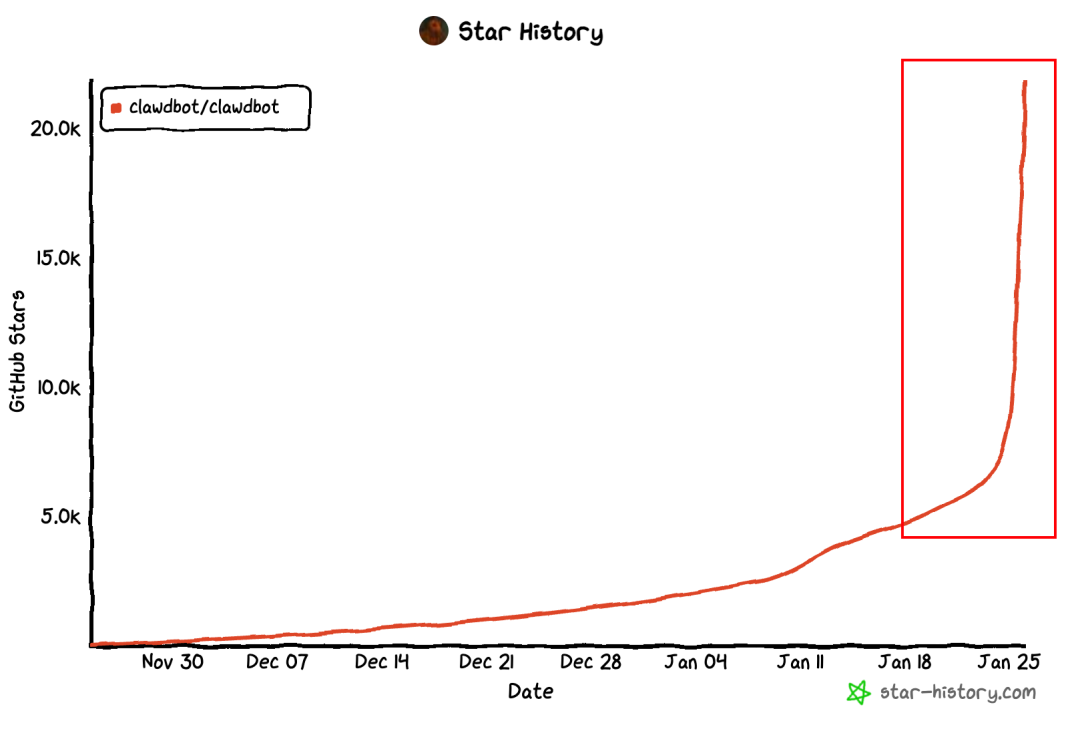
This collective excitement signals a profound shift in the landscape of artificial intelligence. Clawdbot is not merely another large language model (LLM) or a glorified chatbot; it is the first widely adopted Personal AI Agent Gateway. It represents a critical evolution from AI as a consultant—a tool that offers advice and generates text—to AI as an employee—an autonomous entity capable of executing complex, multi-step tasks on a user's local machine. The core thesis of the Clawdbot revolution is that true AI utility is unlocked when the intelligence of an LLM is seamlessly bridged with the capability for operating system-level execution.
Why Clawdbot is the real "AI Agent."
For years, the utility of generative AI has been constrained by what can be termed the "Copy-Paste Loop." Users interact with models like ChatGPT or Claude in a web browser, receive a generated script, email, or code snippet, and then must manually copy and paste that output into a separate application to execute the task. The AI has the brain, but the human remains the hands.
Clawdbot, created by renowned iOS expert and PSPDFKit founder Peter Steinberger, fundamentally breaks this loop. It introduces the concept of an Agent Gateway, a protocol bridge that transforms a passive LLM into a proactive, autonomous system. The system's design is rooted in a philosophy that Steinberger describes as the "Space Lobster" assistant, a 24/7 entity that can be controlled from any messaging platform.
The Agent Gateway paradigm is defined by three key characteristics that distinguish it from traditional AI tools:
1 Proactivity: Clawdbot is not merely reactive. Its "Heartbeat" feature allows it to proactively monitor system states, inboxes, or market conditions and initiate contact with the user (e.g., "You have three urgent emails and a meeting in 20 minutes") .
2 Ubiquitous Control: The system is controlled via common messaging apps like WhatsApp, Telegram, Discord, or iMessage. This eliminates the need for a dedicated application interface, allowing the user to manage their entire digital life from their pocket, regardless of location.
3 Local Execution: The most critical difference is its ability to execute commands directly on the user's operating system via a local shell. This grants the AI the "hands" it needs to move files, run scripts, interact with local applications, and perform real-world automation.
The following table summarizes the functional divergence between the two paradigms:
Feature | Traditional Chatbot (e.g., Web-based Claude) | Clawdbot (Agent Gateway) |
Execution | Suggests steps; requires human copy-paste. | Executes commands directly on the OS. |
Access | Web browser only; session-based. | Ubiquitous via messaging apps (WhatsApp, Telegram). |
Memory | Limited to the current context window; ephemeral. | Persistent, local-first memory (MEMORY.md). |
Proactivity | Reactive (responds to queries). | Proactive (monitors and initiates contact). |
Data Sovereignty | Data stored on vendor's cloud servers. | Data stored entirely on the user's local machine. |
What is Clawdbot's 3-layer architecture
The elegance of Clawdbot lies in its three-layered architecture: the Gateway, the Agent, and the Skill System.
The Gateway: The Central Nervous System
The Gateway is the core of the system, a single, long-running Node.js process that acts as the central hub. It is responsible for:
• Channel Management: Maintaining persistent connections to various messaging platforms (WhatsApp via Baileys, Telegram via grammY, iMessage via imsg CLI).
• Protocol Bridging: Translating incoming natural language messages into a structured format for the Agent.
• Control Plane: Managing the WebSocket connection for the local dashboard and remote nodes (iOS/Android apps).
By running locally, the Gateway ensures that all command routing and data handling remain within the user's controlled environment, upholding the local-first principle.
The Agent, referred to as Pi (a reference to the Raspberry Pi, often used for local automation), is the "brain" that receives the structured command from the Gateway. Pi is a specialized coding agent that uses Remote Procedure Calls (RPC) to interface with the LLM (e.g., Claude 4.5, OpenAI's Codex).
The Agent's true power is realized through the Skill System. Clawdbot's capabilities are not hardcoded but are implemented as plug-and-play modules. The Agent's prompt instructs the LLM to determine which skill is necessary to fulfill the user's request. These skills can range from basic shell access and file manipulation to complex integrations like:
• Browser Use: Autonomous web navigation, searching, and data extraction.
• Application Control: Interfacing with local apps like Obsidian, Notion, or Spotify.
• External APIs: Connecting to services like Gmail, Slack, or even home automation systems like Home Assistant.
The growing ClawdHub acts as a community marketplace for these skills, fostering a viral, self-extending ecosystem.
The Multi-Agent Router
For advanced users, Clawdbot includes a Multi-Agent Routing feature. This allows the Gateway to route different types of requests to specialized LLMs or even different instances of Clawdbot. For example, a user might route all coding requests to a fine-tuned Codex model and all general knowledge queries to Claude 4.5, optimizing both cost and performance.
How Clawdbot solved the LLM memory problem
One of the most frustrating limitations of conventional LLMs is their lack of persistent memory. Every new conversation is a blank slate, forcing the user to repeat context and preferences. Clawdbot addresses this with a novel, local-first memory architecture.
All conversation history, learned facts, and user preferences are stored in a local Markdown file named MEMORY.md. This simple, human-readable file acts as the Agent's permanent knowledge base. When a new query arrives, the system uses Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to search the MEMORY.md file for relevant context and inject it into the LLM's prompt. If you are interested to try by yourself, you can install and build Clawdbot with a spare computer.
This mechanism allows Clawdbot to genuinely "learn" the user over time. A user who asks Clawdbot to order coffee will not be asked their milk preference again if they previously stated, "I only drink oat milk lattes" . This continuous accumulation of context transforms the AI from a transactional tool into a true personal assistant.
However, this design introduces a new, subtle technical challenge: Context Rot. As the MEMORY.md file grows to thousands of lines over months of use, the RAG process must search an increasingly large dataset. This can lead to slower response times, decreased accuracy in retrieving relevant context, and a potential for the AI to "confuse" or "misremember" facts, a phenomenon that remains an active area of research for the Clawdbot community.
Zero-Employee Startup: Real-world hacks and use cases
The true impact of Clawdbot is best illustrated through the real-world use cases that have emerged from the community, demonstrating its potential to create a "Zero-Employee" Company—a business run entirely by a single person and their autonomous AI agent.
• Automating Small Business: One developer shared how he used Clawdbot to manage his parents' tea business. The agent autonomously handled inventory tracking, customer service via messaging apps, automated scheduling, and follow-ups with corporate clients. The agent learned and optimized its processes over time, effectively replacing several administrative roles.
• Vibe Coding and Rapid Prototyping: Developers are leveraging Clawdbot for "Vibe Coding," where a high-level idea is sent via a chat message, and the agent autonomously pulls the code repository, runs tests, generates fixes, and commits the code if tests pass. This dramatically accelerates the development cycle, allowing a single person to manage complex software projects with unprecedented speed.
• Complex Negotiation and Task Switching: In a widely cited example, a user tasked Clawdbot with booking a table at a popular restaurant. When the online booking failed, the agent autonomously switched its strategy, using an ElevenLabs voice synthesis skill to call the restaurant directly, negotiate the reservation, and confirm the booking—all from a single text command.
These examples underscore the economic disruption Clawdbot represents. By automating the entire chain of command—from intent to execution—it allows a single individual, armed with a Mac mini and an API key, to manage the workload previously requiring a small team.
Concerns about Clawdbot's Security, Costs, and Complexity
Despite the hype, Clawdbot is not without its significant risks and barriers to entry. The expert-level discussion surrounding the project centers on three critical issues: security, cost, and technical complexity.
The Security Nightmare: Root Access and Prompt Injection
The core innovation of Clawdbot—its ability to execute shell commands—is also its greatest vulnerability. By granting an AI root access to a personal computer, users are exposed to two major threats:
Prompt Injection: A malicious external message (e.g., a specially crafted email or a message in a group chat) could be interpreted by the LLM as a command to execute a harmful shell script, such as deleting files or exfiltrating sensitive data.
Financial Loss: The community has reported cases, such as the entrepreneur "Sanjay," who lost funds after an insecure Clawdbot configuration was exploited.
The official documentation strongly emphasizes the need for Sandboxing and strict Tool Policies to limit the Agent's access to only necessary directories and commands. Without these safeguards, the user is, in the words of one Reddit deep-dive, "playing with fire".
The Token Tax: The Cost of Autonomy
While the Clawdbot software is open-source and free, its reliance on powerful, proprietary LLMs for reasoning creates a substantial operational cost, or "Token Tax." The 24/7, proactive nature of the agent means it is constantly consuming API tokens.
User Profile | Estimated Monthly Token Cost (USD) | Example Use Case |
Light User | $10 - $30 | Occasional file organization, simple queries. |
Medium User | $30 - $70 | Daily task automation, email filtering, light coding. |
Heavy User | $70 - $150+ | 24/7 monitoring, complex automation, Vibe Coding. |
One prominent developer, Federico Viticci, reported consuming over 180 million tokens in a single week, translating to a bill potentially exceeding $1,000. This high operational cost is a necessary trade-off for the level of autonomy provided.
The Technical Barrier
Despite claims of a "20-minute setup," Clawdbot is not a consumer-ready product. Its installation requires a working knowledge of Node.js, package managers like Nix or pnpm, and the ability to manage API keys and configure complex JSON files for channel and security settings. This technical barrier ensures that, for now, Clawdbot remains primarily a tool for developers, engineers, and highly technical early adopters.
Conclusion
Clawdbot has done more than just sell Mac minis; it has validated a new architectural paradigm for AI. By moving the Agent from the cloud to the local machine and bridging it with ubiquitous messaging channels, Peter Steinberger has delivered on the long-promised vision of a personal, proactive, and autonomous digital assistant.
The future of AI is not just about smarter models, but about better integration with our physical and digital lives. Clawdbot’s success proves that the next frontier is the Agent Gateway, a system that prioritizes local data sovereignty, persistent memory, and, most importantly, the ability to act. While the security risks and high costs demand caution, the Clawdbot revolution has irrevocably set the course for the next generation of AI-driven personal computing.











![Top 10 Meeting Minutes Apps for Different Uses [2026 Shortlist]](https://cdn.shulex-voc.com/shulex/upload/2026-03-08/fcfbef6a-f3e0-4d44-b1fc-7cf1b0e9d380.jpg)

